So, here is where all the action happens.
Main radio of course is housed on the left, it’s partially hidden under my currently over-populated breadboard.
All 3 monitors are linked to the same PC, using a pair of video cards. This is a very flexible system with so much screen real estate.
Main system power is provided by the pair of power supplies next to the radio – these are homebrew units using surplus switched mode PSU boards. Check my previous posts for more details.

The main power supply system. These two supplies are cross connected, giving a total DC amperage of 30A at 13.8v. There is also a link to a large 220Ah lead-acid battery bank (orange cable), to keep me on the air during power outages. This cable is getting upgraded to something more beefy shortly. The white cable is currently supplying power to my online radiation monitor.
The main high-current DC outputs are the Speakon connectors next to the meters. The top one is powering the radio directly, the bottom is linked through to my 12v distribution box for lower current loads, such as the oscilloscope, audio amplifiers, tools, etc.
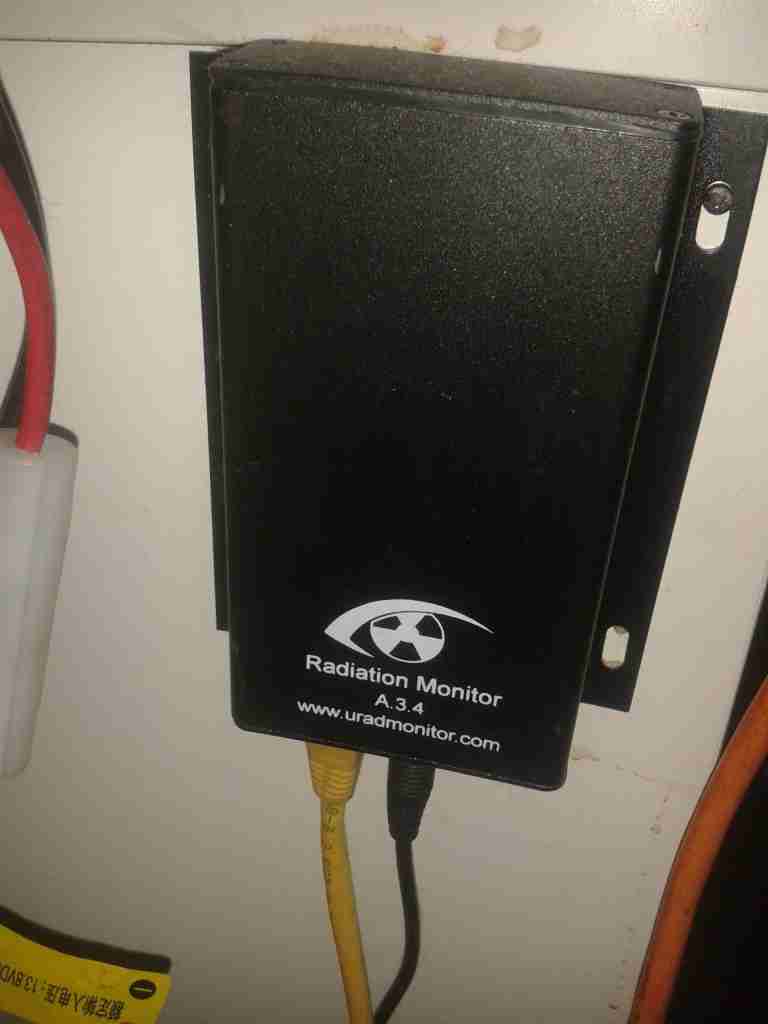

Attached to the side of the desk is the radiation monitor itself.
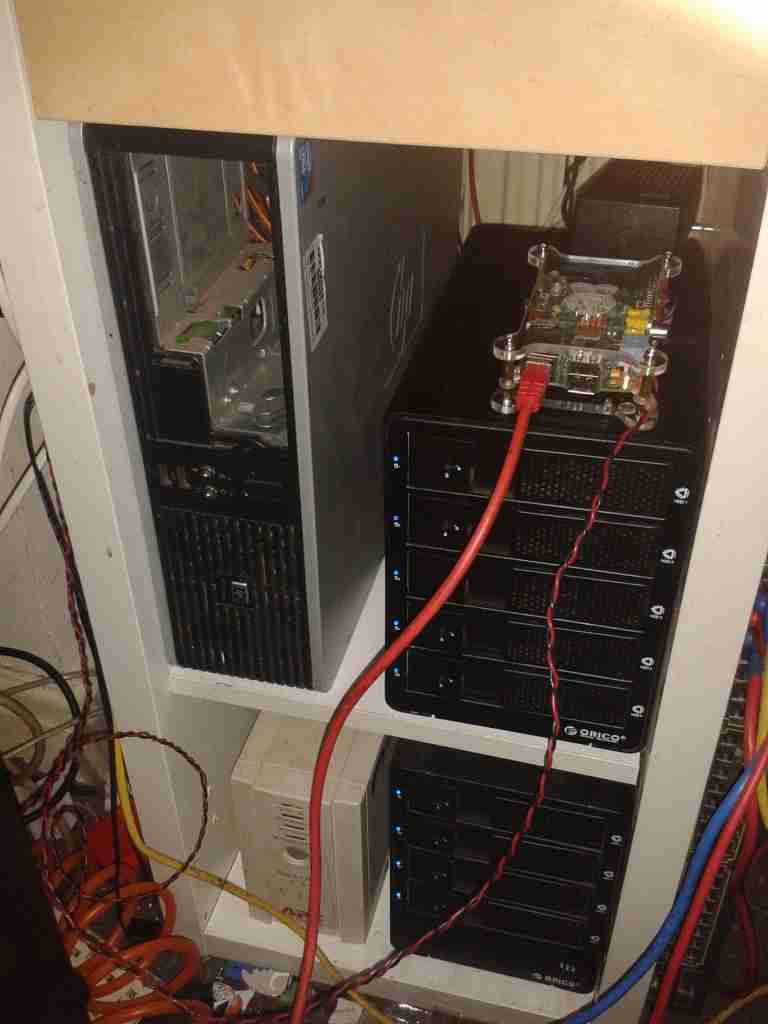

Under the radio is the core NAS of the network. It’s an array of 9 4TB disks, in RAID6, giving a total capacity after parity of 28TB. This provides storage & services to every other machine in the shack, the Raspberry Pi on top of the disk array is doing general network housekeeping & monitoring, also generating the graphs for the Radiation Monitor page. A Cisco 48-port switch is partially out of frame on the right, providing 100MB Ethernet to the devices that don’t require gigabit.