Random teardown time!
The OPN-2001 is a very small handheld barcode data collection device, used for stock keeping, inventory, etc.
It’s powered by an internal Li-Poly cell, at 150mAh, and has storage for 1000 barcodes in it’s internal memory.

The unit is charged via it’s USB port, the data can also be downloaded using this interface.

Here’s the bottom of the unit with it’s label. Serial number removed to protect the guilty. 😉

Here the bottom cover has been removed from the scanner, showing the internals. The barcode engine is on the left, this contains all the hardware & logic for scanning & storing the barcode data. The Li-Poly cell is under the FFC cable wrapped in foam tape for protection.

Here’s the PCB & engine assembly removed from the casing. The lower PCB appears to just handle the user interface buttons, beeper & USB power & charging circuitry. All the processing logic is on the barcode engine itself.

Here’s the back of the support PCB, with the pair of buttons for scanning & deleting barcodes. Also on this board is a 32kHz clock crystal & a Ricoh RV5C386A RTC IC. This communicates with the main processor via I²C for storing the date & time with the barcodes. At the bottom right corner are some of the power supply passives.

Here’s the other side of the support PCB, with the beeper, battery connector & the switching regulator to provide the barcode engine with 3.3v power.

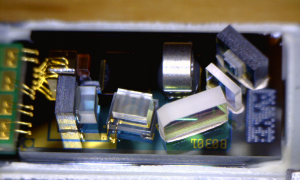
Here’s the barcode engine itself, which is absolutely tiny, at roughly 20mm square. The main processor & it’s associated Flash ROM are on this PCB. The main processor has an ARM7 32bit core, with 64kB of RAM, and onboard 512kB of ROM for program & barcode storage.

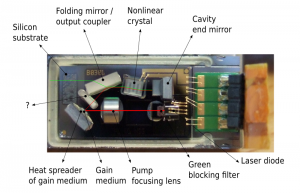
Here’s the business end of the barcode engine, the mirror vibrates at 100Hz to produce the scan line. The laser diode is rated at 1mW, 650nm. This is in the deep red range.