Well, it’s time for another viewfinder hack! I’ve been after one of these for a while, this is from an early 1980’s era Sony Trinicon camera, and instead of the tiny ½” round CRT display, these have a 1.5″ square CRT – a Matsushita 40CB4. Luckily I managed to score a pair of these from eBay for very little money. Update: The second camera’s viewfinder module turned out to have a dead flyback transformer, but at least I have a good spare CRT & the rest of the support components. More to come later on the teardown of the camera itself.

The eyecup assembly with the magnifying lens & turning mirror is easy to remove, with clips & a single screw holding it onto the CRT holder sticking out of the side of the main casing.

Removing some screws around the case allows the top cover to be removed, revealing the electronics. There’s certainly more in here than the later camera viewfinders, in this unit there are two boards slotted together with a board-to-board interconnect at the bottom. The CRT is at the top of the photo, hiding inside the plastic housing & deflection yoke assembly.

Here’s the CRT & one of the control boards removed from the case, having been stripped of the heatshrink tube that held the final anode lead in place. Just like on larger CRTs, this viewfinder has the final anode on a cavity connector fused into the bell, instead of being led out to a pin on the base. This is probably due to the much higher anode voltage of 5kV, a big jump from the 2kV on the ½” round tubes.

Yup, it’s definitely the elusive 40CB4. Apparently these CRTs are still manufactured to this day for professional camera viewfinders, as the resolution of this small vacuum tube is still better than similarly sized modern tech such as LCDs or OLEDs. The phosphor used is type P4 – ZnS:Ag+(Zn,Cd)S:Ag, with an aluminized overcoat.

After the base connector & deflection yoke are removed from the tube, the very long neck can be seen, this long glass neck apparently giving better focus & resolution than the stubbier tubes.

The electron gun is the usual single unit as usually found in monochrome tubes.

The bottom board in the assembly has all the control circuitry for the CRT, including the HA11244 deflection IC, composite sync separator & vertical deflection drive circuit. There are also circuits here to display a video waveform on the CRT, along with iris & white balance markers.

The other board has the horizontal drive circuitry, along with the video input amplifier. Despite the attempt to miniaturize the entire assembly, these are still well packed boards. Some of the resistors & diodes are bussed together in custom SIL hybrid modules to save PCB space. Like all the other CRT viewfinders, these units are meant for viewing via a mirror – the horizontal deflection coil connections need to be reversed to show a correct image without the mirror. The Red & Blue wires to the yoke need to be swapped here.

The horizontal board on this unit also supports the flyback transformer, which is massive compared to the other viewfinder circuits. Biasing, focus & filament supplies for the CRT are also derived from this transformer, via auxiliary windings.

The boards slot together in the centre to form the fully operational circuit.
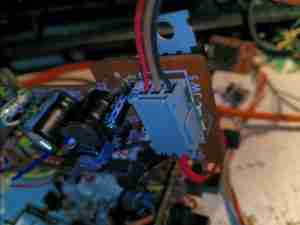
Out of the 3 plugs emerging from the cable feeding the viiewfinder, only this one is important, on the horizontal drive board. Black is ground, Brown +8.5v & red is composite video input. There’s also a resistor tied into the positive rail to the video input pin, which pulls it high to 8.5v – this is R1 right next to this connector. Desolder this 22K resistor to help protect anything feeding a signal into the unit, like a RPi, it’s not needed for normal operation.

As usual for a CRT post, the Fallout loading screen on the display. The picture quality isn’t as good as it should be, probably due to the noisy buck-converter I have rigged up for testing. If it doesn’t get better with a linear regulator, I’ll start replacing the 39 year old electrolytic capacitors. Current draw is 130mA at 7.5v. Schematics for this unit & the CRT datasheet are available below: