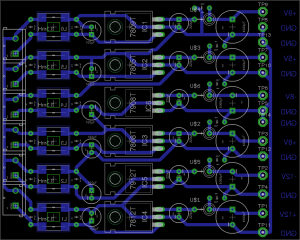
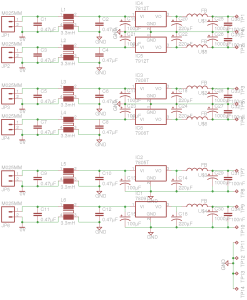
Since I’ve discovered some nice high power PSUs in the form of Playstation 3 PSUs, it’s time to get a new Bench PSU Build underway!

I’ve gone for the APS-227 version as it’s got the 32A rail. This makes things slightly beefier overall, as the loading will never be anywhere close to 100% for long, more headroom on the specs is the result.

The case I’ve chosen for this is an ABS desktop instrument case from eBay, the TE554 200x175x70mm. The ABS is easy to cut the holes for all the through-panel gear, along with being sturdy enough. Aluminium front & back panels would be a nice addition for a better look.

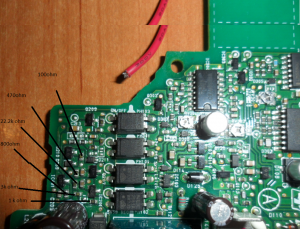
The PSU board is removed from it’s factory casing & installed on the bottom shell half, unfortunately the moulded-in posts didn’t match the screw hole locations so I had to mount some brass standoffs separately. The AC input is also fitted here, I’ve used a common-mode filter to test things (this won’t be staying, as it fouls one of the case screw holes). The 40A rated DC output cable is soldered directly to the PCB traces, as there’s no room under the board to fit the factory DC power connector. (This is the biggest case I could find on eBay, and things are still a little tight). Some minor modifications were required to get the PCB to fit correctly.

I decided to add some limited voltage adjustment capability to the front panel, I had a 100Ω Vishay Spectrol Precision 10-turn potentiometer in my parts bin, from a project long since gone that just about fits between the panel & the output rectifier heatsink. The trimpot I added when I first posted about these PSUs is now used to set the upper voltage limit of 15 volts. (The output electrolytics are 16v rated, and are in an awkward place to get at to change for higher voltage parts). The binding posts are rated to 30A, and were also left over from a previous project.
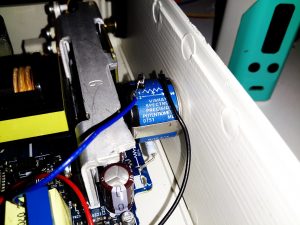
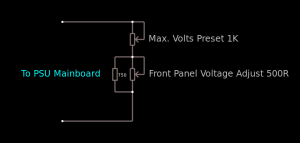
This front panel potentiometer is electrically in series with the trimpot glued to the top of the auxiliary transformer, see above for a simple schematic of the added components. In this PSU, reducing the total resistance in the regulator circuit increases the voltage, so make sure the potentiometer is wired correctly for this!
After some experimentation, a 500Ω 10-turn potentiometer would be a better match, with a 750Ω resistor in parallel to give a total resistance range on the front panel pot of 300Ω. This will give a lower minimum voltage limit of about 12.00v to make lead-acid battery charging easier.
I’ve had to make a minor modification to the output rectifier heatsink to get this pot to fit in the available space, but nothing big enough to stop the heatsink working correctly.

Here I’ve got the binding posts mounted, however the studs are a little too long. Once the wiring is installed these will be trimmed back to clear both the case screw path & the heatsink. (The heatsink isn’t a part of the power path anyway, so it’s isolated).

To keep the output rectifier MOSFETs cool, there’s a fan mounted in the upper shell just above their location, this case has vents in the bottom already moulded in for the air to exit. The fan is operated with the DC output contactor, only running when the main DC is switched on. This keeps the noise to a minimum when the supply doesn’t require cooling. The panel meter control board is also mounted up here, in the only empty space available. The panel meter module itself is a VAC-1030A from MingHe.

The measurement shunt & main power contactor for the DC output is on another board, here mounted on the left side of the case. The measurement shunt is a low-cost one in this module, I doubt it’s made of the usual materials of Manganin or Constantan, this is confirmed by my meansurements as when the shunt heats up from high-power use, the readings drift by about 100mA. The original terminal blocks this module arrived with have been removed & the DC cables soldered directly to the PCB, to keep the number of high-current junctions to a minimum. This should ensure the lowest possible losses from resistive heating.

The panel meter module iself is powered from the 5v standby rail of the Sony PSU, instead of the 12v rail. This allows me to keep the meter on while the main 12v output is switched off.

here’s the supply with everything fitted to the lower shell – it’s a tight fit! A standard IEC connector has been fitted into the back panel for the mains input, giving much more clearance for the AC side of things.

With the top shell in place, a look through the panel cutout for the meter LCD shows the rather tight fit of all the meter components. There’s about 25mm of clearance above the top of the PSU board, giving plenty of room for the 40mm cooling fan to circulate air around.

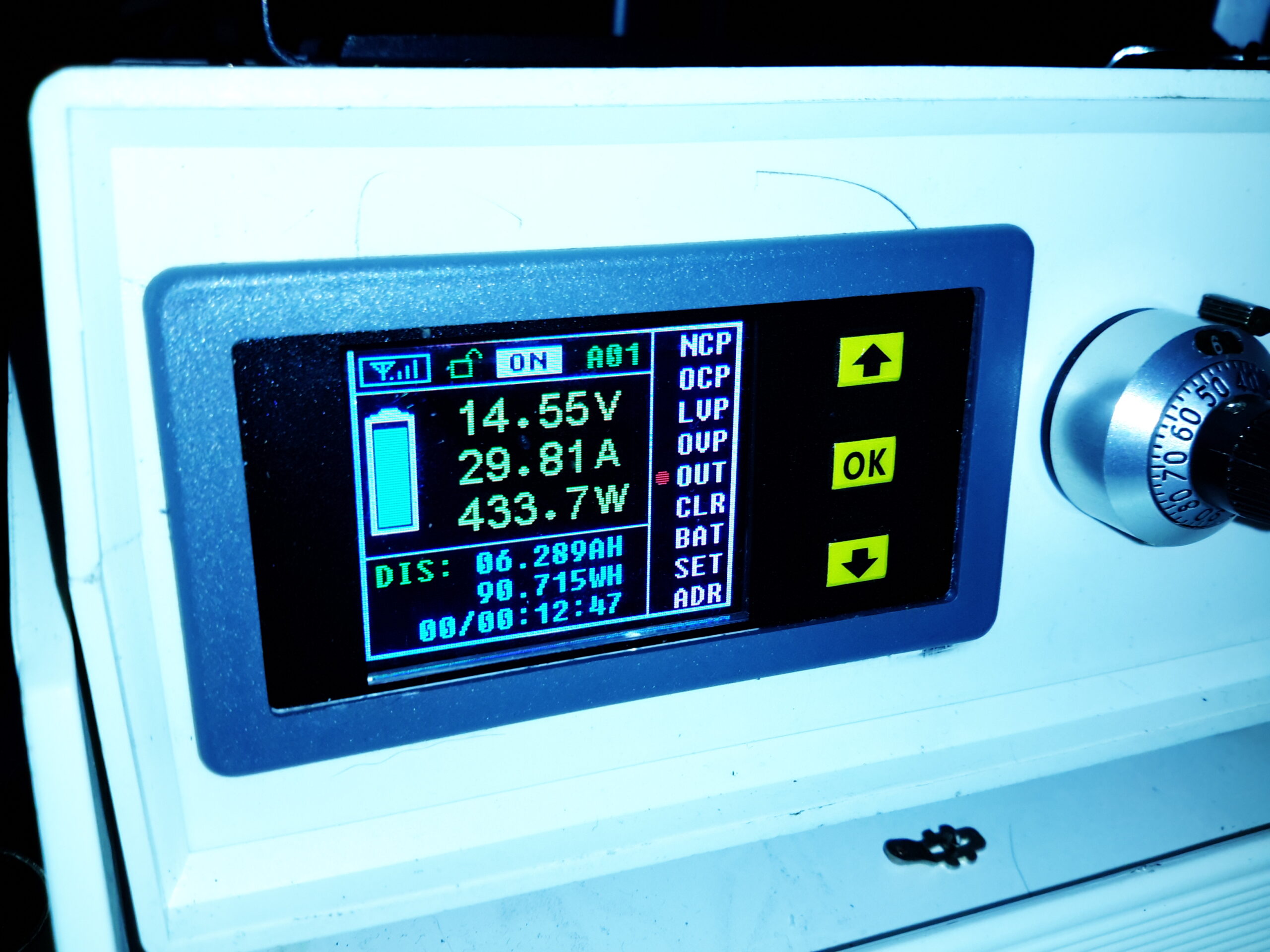
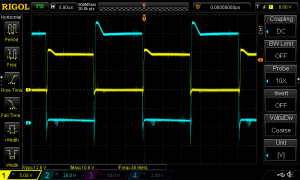
Here’s the finished supply under a full load test – it’s charging a 200Ah deep cycle battery. The meter offers many protection modes, so I’ve set the current limit at 30A – preventing Sony’s built in over current protection on the PSU tripping with this function is a bonus, as the supply takes a good 90 seconds to recover afterwards. I’ll go into the many modes & features of this meter in another post.